Professor at the University of Washington: Artificial blood can replace human blood
The shortage of blood products has been a problem due to insufficient blood donation and the threat of AIDS and other pathogenic bacteria. Thanks to the application of some new technologies, artificial blood may be widely used in emergency surgery and blood disease treatment ten years later to solve the long-standing shortage of blood products.
Scientists have been working hard to develop artificial blood that replaces some or all of the functions of blood. However, this seemingly simple red viscous liquid cannot be easily imitated, let alone surpassed. Fortunately, scientists are more frustrated and more courageous, thanks to the addition of some new technologies, and may soon be able to crack this major medicine. problem. The author explains the latest trends and developments in this cutting-edge biotechnology.
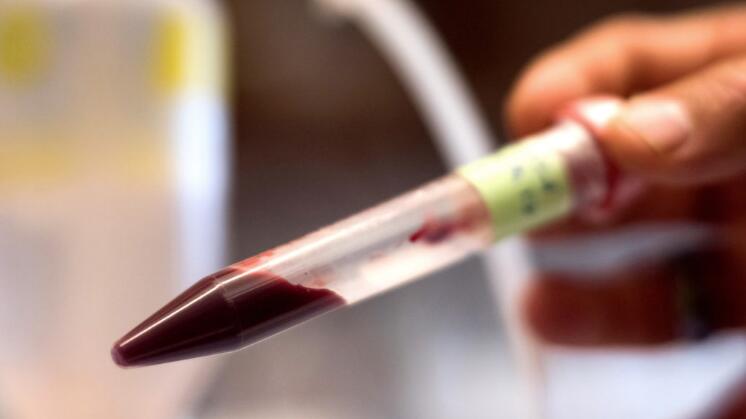
Artificial blood developed by Dr. Allan's Docotor laboratory can be freeze-dried into a powder and then mixed with sterile water when needed.
Instantly soluble artificial blood powder: upcoming human blood substitute test
A scene in Dr. Allan's lab in St. Louis - while injecting red blood cells into a test tube, people use tiny tools to measure the rabbit's aortic response and calculate the contraction strength of the aorta. Dr. Allan and his team are working hard to ensure that the rabbit aorta is reflected in the rabbit's aorta after injection of the artificial blood developed by the rabbit.
The recent trials are not only part of the many trials conducted by the team, but also means that after these several trials, blood tests will be performed on the human body. At the same time, it also shows the initial steps of its experimental concept, accompanied by good luck, these ideas can make it out of the field of failure in the field for decades.
“In order to develop blood substitutes, people have worked hard for fifty or six decades, but nothing has been achieved.†A paediatric intensive care physician said that he is also a researcher at Washington University in St. Louis.
The demand for this product is clear. Blood loss caused by traumatic injuries causes thousands of deaths each year, and even if the injured survive, hypoxia can cause permanent damage to the tissue. Fresh blood can only be stored for 42 days and can only be stored for several hours without freezing. Blood substitutes are critical for areas such as battlefields or remote locations. These places are not easy to get blood, and the use of blood substitutes can temporarily temporarily allow the injured to maintain their lives before being taken to the hospital.
However, researchers from the academic and biopharmaceutical industries have been hit hard on the road to developing blood substitutes. Several companies have abandoned the study, including Baxter, Northfield Laboratories and Biopure. Researchers of artificial blood are not developing a true blood substitute because they do not have all the functions of blood, but rather provide a way to deliver oxygen to the body.
A key issue is that hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that delivers oxygen from the lungs to tissues that require oxygen in the body, but it can destroy tissue and cause blood vessels to contract. This is why hemoglobin is inside the cell, in order to isolate hemoglobin and toxic iron.
Any successful blood substitute will avoid the damage caused by hemoglobin while delivering oxygen. In past attempts, scientists have attempted to improve hemoglobin to make it safer, but so far, no blood substitutes have been approved for use in the United States or Europe. (Hemopure is a product of oxygen therapy and is a blood substitute used in South Africa. A clinical trial based on stem cell replacement is expected to be conducted in the UK this fall.)
Dr. Allan and his colleagues did not modify hemoglobin, which they encapsulated in a synthetic polymer designed by Dipanjan Pan, a collaborator with Dr. Allan, from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.

Dr. Allan, at his office in Washington University in St. Louis, tried to develop an artificial blood that could be used in hospitals without blood donation.
Black Bean Salted,Salted Dried Black Bean,Temple Salted Black Bean,Black Salted Bean
jiangmen city hongsing food co., ltd. , https://www.jmhongsing.com