Application of DSC-Raman Combined Technology in Studying Polymer Crystallinity
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Raman spectroscopy are widely used in the study of crystallinity, but the principles of monitoring are quite different. The DSC not only accurately determines the crystallinity of the sample, but also obtains the crystallization kinetic parameters by measuring the relevant enthalpy change information. With its extremely excellent temperature control capability – heating and cooling rates can be controlled up to 750 ° C / min, PerkinElmer ® DSC 8000 or 8500 DSC is often used for crystallinity studies. The patented double furnace design gives the furnace temperature an instant stability and the ability to precisely control at a real temperature. Isothermal studies are best performed in this mode. The Raman spectrum of the crystal is generally different from the amorphous material, and the former has a narrow peak width. Raman spectrometers can also be used to monitor very slow changes, providing additional sample information and accurately determining where the mixed crystals occur. The RamanStationTM 400 and RamanFlex TMlines developed by PerkinElmer allow for real-time adjustment of the laser pulse period, making it easy to adjust the best match between Raman spectral acquisition signal rate and DSC scan rate. Simultaneous measurement eliminates the uncertainty that may be caused by the material's thermal history.
The DSC-Raman detection for semi-crystalline polyoxyethylene below can fully demonstrate the complementarity of the two techniques. These materials have been widely used in all aspects of medical care, life and work, such as toothpaste. The sample was heated from 10 ° C to 75 ° C, subjected to a melting process, then cooled to 10 ° C and then repeatedly scanned. The melting peak temperature of the sample in the first week of the cycle was at 70 ° C and at 66.7 ° C in the second temperature sweep. The value of the heat of fusion measured during the second week of temperature rise also decreased (Fig. 1). This implies that the first melting and crystallization process increases the amorphous zone of the material. 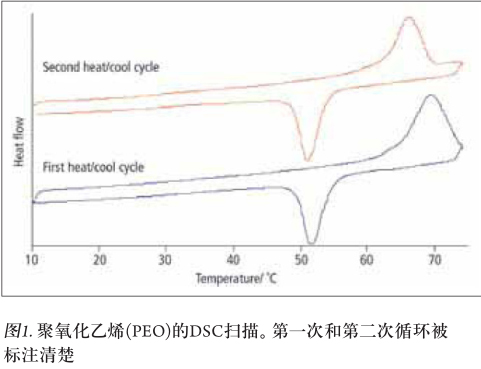
The Raman spectrum is accepted every 5 seconds at the time of DSC operation. After the first heating/cooling cycle, a large number of amorphous component characteristics were shown in the spectrum (Fig. 2). By subtracting, the spectral difference before and after the scan can be cycled for the first time. Although there is noise, it is very similar to the spectrum when it is completely melted. Therefore, the Raman spectrum can directly confirm the inference from the DSC data, that is, the first heating/cooling cycle increases the amorphous content of the sample. 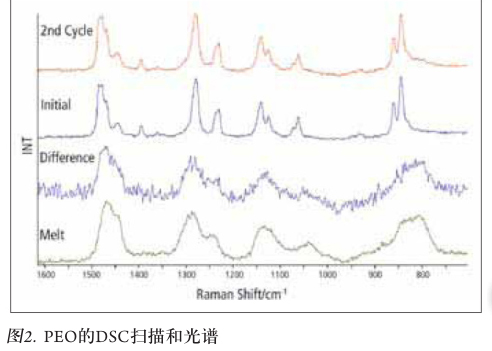
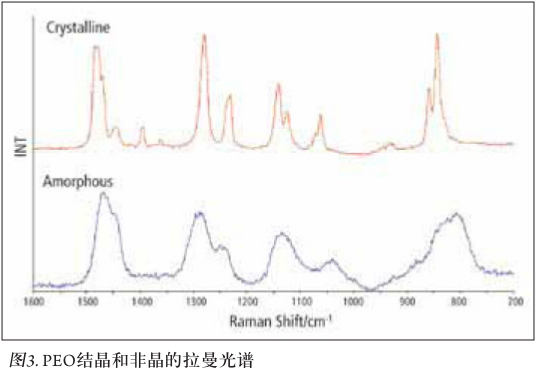
The DSC-Raman spectrometer gives us the ability to accurately study high polymers, which can efficiently reproduce the crystallization behavior of samples under various temperature control conditions, and the structural information related to DSC energy changes can also be reflected by Raman spectroscopy. This approach makes the correlation between the two methods accurate and contributes to a deeper understanding of the crystallization behavior.
For details, please click the button below to request information.
Eas anti-theft antenna is mainly suitable for large supermarkets, shopping malls, bookstores, audio stores with Security hard tags, rf soft label, AM lable,Pin and Lanyard, eas detacher, Hook Lock ,EAS Self Alarm Tag, EAS Safer Box,etc.
Rf Hard Tag ,Anti Theft Hard Tag,Hard Tag Sensor,Sensormatic Hard Tags
Wenzhou Boshine Electronic Security Co. Ltd , https://www.boshine.com