Ginseng has been regarded as a god grass since ancient times and has been regarded as a magical medicine with many curative effects for thousands of years. With the development of modern pharmacology and laboratory testing technology, the process of ginseng acting on the metabolism and functioning of the human body has gradually become clear. At present, we find that the main component of ginseng is ginsenoside - ginsenoside is a sterol compound that exerts anti-tumor, anti-hypertensive, anti-viral and immunomodulatory equivalent energy by affecting multiple metabolic pathways.
At the beginning of this year, Jilin University came to the good news of ginsenoside research to achieve new results. A team of Jilin University successfully discovered the human target of ginsenoside, which provided important clues for the anti-tumor efficacy of certified ginseng. Some of the results of this topic have been published in the "Science Report", an open book of Nature, which is the first report on the human target of ginsenosides. To achieve such results, it can be said that modern laboratory testing technology is indispensable.
There are more than a dozen ginsenosides, which are classified into two types, dammarane type and oleanane type, depending on the glycosyl structure. The changes in the class and content of ginsenosides lead to differences in the clinical efficacy and clinical application of different tissues of ginseng such as roots and rhizomes. Therefore, studying the spatial distribution of different ginsenosides in tissues can provide more reference information for the clinical application of ginseng. Conducive to understanding and improving the breeding and cultivation of ginseng.
At present, a leading direction in the industry is the detection of ginsenosides by Desorption Electrospray Ionization (DESI). DESI is a fast mass spectrometry imaging technology in atmospheric conditions. Compared to other mass spectrometry imaging techniques such as MALDI, DESI requires almost no pre-treatment of the sample (eg, grinding, extraction, derivatization, etc.), so it can truly reflect the distribution of the compound in the sample.
experimental method
Sample Preparation:
The main root of 4-year-old IR826 ginseng was used to prepare 20 μm frozen transverse sections for DEESI mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry method:
Mass Spectrometry System: Waters Xevo G2-XS Tof
Ionization mode: ESI-
Capillary voltage: 4.5 kV
Taper hole voltage: 80 V
Mass scan range: m/z 100-1200
Spray solvent:
♦ 90% MeOH
♦ 10% H2O
♦ 0.1mM NH4Cl
♦ 0.1 mM leucine enkephaline (lockmass, m/z 554.2615)
Spray flow rate: 1.5 μL/min
Pixel size: 100 μm x 100 um
Scanning speed: 400 μm/s
Mass Spectrometry Data Imaging: Waters HDImaging
Through this method, we can get:
The cross section of ginseng can be divided into three parts, the outermost periscope (Periderm), the inner cortex (Cortex), and the inwardly located middle part (Stele) (Fig. 1a). The DESI mass spectrometry was performed on the cross section of ginseng. The ginsenosides including Rg1/Rf, pseudo-Rc1, Ra1/Ra2, Rd/Re, Rs1/Rs2 and Ra3 can clearly see the signal (Fig. 1b), and the Rg1/Rf is highly distributed. In the pericarp and middle column, Rd/Re, Rs1/Rs2, Ra1/Ra2 and pseudo-Rc1 are highly distributed in the pericarp, and the content in the middle column is lower, while Ra3 exhibits a more diffuse distribution pattern near the outer skin. The regional distribution is higher (Fig. 2c). Similarly, the distribution of other metabolites such as maltose and Citbismine C contained in ginseng is also evident (Fig. 2c).
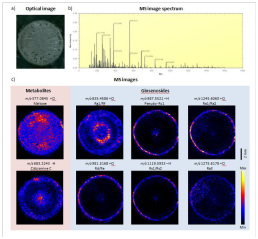
Figure 1. Distribution of ginsenosides in transverse sections of ginseng roots based on DESI mass spectrometry . a) Optical image of transverse sections of ginseng roots. b) Total mass spectrum. c) Maltose, Citbismine C and ginsenosides include DESI mass spectrometry imaging results of Rg1/Rf , pseudo-Rc1, Ra1/Ra2, Rd/Re, Rs1/Rs2 and Ra3 .
Further, the distribution of isomers such as Rg1/Rf and Rd/Re in ginsenosides was investigated by DESI-MS/MS imaging method. Taking Rg1/Rf as an example, Rg1 is cleaved at the monosaccharide group to obtain the characteristic fragment m/z 637.46, and Rf is cleaved at the disaccharide group to obtain the characteristic fragment m/z 457.15 (Figs. 2a and 2b), Rg1 and Rf The DESI-MS/MS imaging results showed a distinctly different spatial distribution (Fig. 2c).
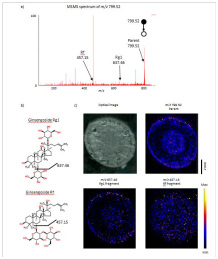
Figure 2. DESI-MS/MS imaging results of Rf and Rg1 in transverse sections of ginseng roots 3 . a ) MS/MS spectrum of Rf/Rg1 (m/z 799.52) . b) Molecular structure of Rf and Rg1 . c) DESI-MS/MS imaging of Rf and Rg1 .
By this method, it can be seen that DESI imaging technology can directly obtain the information of metabolites in the sample under the condition that the sample is not required to be pre-processed, thereby truly reflecting the spatial distribution of the compound. Here, we applied DESI imaging technology to analyze ginsenosides in ginseng horizontal sections and found that different ginsenosides have their own specific distribution. At the same time, DESI-MS/MS imaging technology can further distinguish the distribution of ginsenoside isomers.
Isoprene Gasket
Our medicinal synthetic polyisoprene gasket for injection does not contain any substances that can easily produce pyrogen. We now use a unique technique to add cytotoxicity to the routine test of butyl rubber stoppers such as pyrogen, hemolysis, acute systemic toxicity test and so on. Systemic injection test and intradermal stimulation test have been used abroad for many years.Our good puncture resistance ensures the minimum rate of chip drop during the puncture process and our good self-sealing performance can guarantee no leakage during using process in hospital.Also,good retention of puncture device ensures that there is no needle slider and needle drop in the process of hospital use.
Isoprene Gasket, Medical Synthetic Isoprene Gasket, Pharmaceutical Polyisoprene Disc, Pharmaceutical Synthetic Disc, Gasket for syringe, syringe piston, syringe rubber
Suzhou CRH New Material Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.crh-health.com

