Surface plasmon resonance OpenSPR improved peptide screening research method
In the first phase of any treatment development project, it is necessary to use a sophisticated model system to review newer treatments. Use a stable model system to compare new treatments. Building a model system will provide the basis for effective screening analysis, enabling researchers to effectively compare and contrast the various biological changes of the therapeutic agents of interest to them. Importantly, hyaluronic acid-mediated motor receptors, also known as RHSMM, are commonly overexpressed in breast, colorectal and prostate cancers. It has been shown to be a contributor to two of the six cancer markers, angiogenesis and invasion/metastasis. Notably, RHAMM has been identified as a biomarker for some highly aggressive cancers. In this regard, therefore, the development of highly specific therapeutic drugs targeting RHAMM can inhibit angiogenesis and invasion/metastasis, thereby limiting the spread of certain aggressive tumors. Unfortunately, the use of recombinant protein technology is essentially ineffective for adequate production and isolation of full-length RHAMM proteins, which is critical for in vitro binding studies.
Dr. Leonard Luyt et al. used OpenSPR local surface plasmon resonance technology to obtain the key data needed for their newly discovered cancer treatment development, and published an article in September 2018 entitled "A truncated RHAMM protein for discovering novel therapeutic The peptides", the data obtained by OpenSPR were observed for their chemically synthesized 7kDa RHAMM "mini-protein" binding behavior, which was engineered and used to screen for candidate therapeutic peptides.

Summary
RHAMM is a large 95kDa carbohydrate-binding protein that is responsible for many cellular processes, including cell movement, tissue repair, and triggering innate immune responses. However, when overexpressed, RHAMM has been discovered in two major carcinogenic processes, including stimulation of angiogenesis (angiogenesis) and cell invasion and spread (invasion/metastasis). Historically, full-length RHAMM has been very difficult to produce and isolate for meaningful in vitro studies. Because it plays an important role in tumorigenesis, it is clear that RHAMM is critical for research.Further, hyaluronic acid (HA) is a high molecular weight polysaccharide and is present in a high concentration in the extracellular matrix. At the time of fragmentation, HA tends to accumulate and previous studies have demonstrated that these fragmentation accumulation patterns are homologous during angiogenesis. RHAMM tends to bind to HA and subsequently interact with CD44 (and some growth factor receptors). In turn, many known cancer pathways have been activated, including the RAS, ERK and MEK pathways. These pathways are primarily responsible for uncontrolled cell growth, angiogenesis and cell trafficking. It is worth noting that the above pathway-dependent events are three of the six cancer markers. Notably, the difficulty in producing and isolating full-length RHAMM proteins, coupled with the effect of HA-RHAMM binding in subsequent oncogenic pathways, suggests the need to develop an alternative system to screen for potential RHAMM therapeutic interferences.

In this article, the researchers synthesized a 7kDa RHAMM "mini-protein" by Fmoc solid phase peptide, followed by circular dichroism analysis of the structure of the truncated RHAMM. It should be noted that the truncated RHAMM mini-protein was designed to contain only HA binding sites, but a negative control without critical residues required for HA binding was also designed. After synthesis and structural analysis, binding kinetics and affinity constants between the 7 kDa RHAMM mini-protein and its natural ligand HA were then examined using OpenSPR surface plasmon resonance. In addition, many tubulin-derived HA peptide analogs known to bind to recombinant RHAMM are also used to demonstrate the binding ability of the synthetic RHAMM mini-protein.
Importantly, Nicoya's SPR study demonstrated that the 7kDa RHAMM mini-protein is an excellent alternative to the generation and isolation of full-length recombinant RHAMM, so future research on this important carcinogenic factor is much lower.
OpenSPR's help for this research
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to resolve the interaction between the truncated RHAMM protein, HA and the tubulin-derived HA peptide analog. It is worth noting that many experiments have been performed on OpenSPR and many different surface chemical sensor chips have been used. First, the common gold chip was incubated with cystamine-functionalized HA for 3 days and blocked to prevent non-specific binding. A functional RHAMM mini-protein and the corresponding negative control (Ala-RHAMM) were used as analytes. Subsequently, the RHAMM mini-protein with the C-terminal His tag was immobilized on an NTA chip and detected using all of the tubulin-derived HA peptide analogs as analytes.Importantly, this binding data clearly indicates that the chemically synthesized RHAMM mini-protein can be an effective alternative to screening for anti-cancer peptide candidates for disrupting the RHAMM-HA-CD44 binding response. In this regard, the OpenSPR binding data provides quantitative evidence that the tedious work of reconstituting the full-length RHAMM protein may not be required. In addition, by using OpenSPR, researchers can obtain SPR data from their own lab platform to help them speed up research and publish their findings faster.
SPR is an unlabeled detection technology that allows researchers to quantify the binding between two biomolecules. The SPR technique allows us to determine the interactions of kon, koff and KD, and provides a deeper understanding of the interactions between molecules than other techniques that only provide endpoint measurements, such as pull-down experiments. SPR is not only necessary for publishing articles, but also necessary for the development of many medical and medical research fields. As shown in the following figure, the number of articles published by SPR data has increased significantly in recent years. 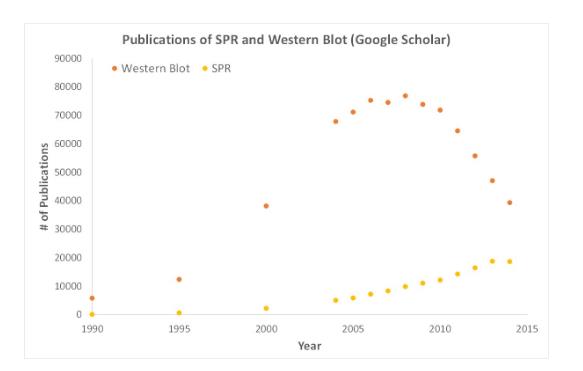
Scientific publications involving SPR have increased drastically over the years. SPR has become fundamental for publications while traditional techniques like Western Blots are becoming less important.
OpenSPR is a user-friendly and low-maintenance, low-tech threshold for next-generation SPR solutions that are currently used by hundreds of researchers. With LSPR technology at your fingertips, you can get the quality data you need while speeding up your research and publishing!

Advantages of Nicoya OpenSPR Molecular Interaction Analyzer in Improving Peptide Screening Research
• Easy to operate - 1 hour to control;
• Complete kinetic parameter detection - Ka, Kd, ​​KD;
• High efficiency---loading, results, one-click analysis, results in 10min, complete kinetic test results in 1-2h;
• High precision – detection is not affected by temperature and buffer refractive index;
• No need for dedicated correction channels – negligible bulk effects;
Hotel Safe Box,Password Hotel Safe Box,Hotel Electronic Safe Box,Safe Box Hotel Room
Hebei Yingbo Safe Boxes Co.,Ltd , https://www.ybsafebox.com