Detection of Escherichia coli O157 in frozen drinks
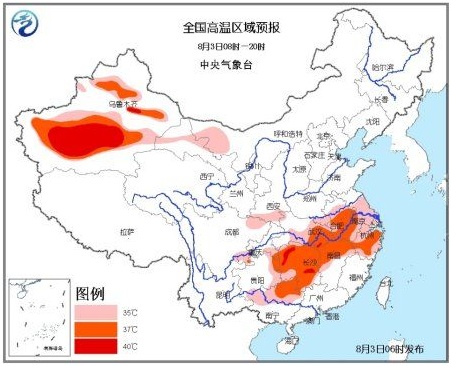
Summer has arrived, and the “barbecue mode†has entered the country. On April 23, Guangzhou entered the summer; on May 14, Beijing entered the summer; on May 29, Shanghai entered the summer. The picture below shows a high-temperature area map released by the China Meteorological Network on August 3. The high-temperature area represented by red occupies a considerable proportion.
In the hot summer days, delicious and cool cold drinks can make you forget the heat and heat. Various brands of ice cream, popsicles, sodas, juices and other products on the market are dazzling, which greatly enriches the material life of the people. However, the preservation of cold drinks requires attention. It usually needs to be stored at 4 ° C. Some ice products need to be stored at -20 ° C. Once these cold drinks are thawed and then re-frozen, there may be bacteria in them.

The Chinese national standard "GB 2759.1-2003 Hygienic Standard for Frozen Drinks" has specific requirements for microbial content. The following table provides specific information:
project | Total number of colonies (cfu/mL) | Coliform (MPN/100mL) | Pathogenic bacteria |
Milk protein-containing frozen drink | ≤ 25000 | ≤ 450 | Not checked out |
Bean-containing frozen drinks | ≤ 20000 | ≤ 450 | Not checked out |
Frozen drinks containing starch or fruit | ≤ 3000 | ≤ 100 | Not checked out |
Eating ice cubes | ≤ 100 | ≤ 6 | Not checked out |
E. coli is commonly referred to as E. coli. These bacteria are often found in the digestive tract of humans and animals and are excreted with feces and are widely distributed in water and soil. Most enterobacteria belong to the normal flora, and when the body's immunity is reduced or invaded into the extraintestinal tissues, it becomes a conditional pathogen and causes disease. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) is a group of Escherichia coli that causes hemorrhagic diarrhea and enteritis in humans. The O157:H7 serotype is used as a representative strain. According to relevant standards, Escherichia coli O157 should not be detected in frozen drinks.
According to the corresponding standards, RephiLe especially recommends the following Escherichia coli O157 detection solution for frozen drinks. The detection protocol is a typical colony isolated on the surface of a solid medium according to international standards. The colony can react with the product and cause agglutination of O157 serum:
First, the instrument
Dry heat sterilization box and moist heat sterilizer; incubator; PH meter; sterile inoculating loop; pipette; magnetic rack; rotary mixer; Direct-Pure UP ultrapure water system.
Second, the reagent
Enrichment solution: mTSB + N (modified tryptone soy broth mTSB + novomycin solution); CT-SMAC medium; nutrient agar; trypsin medium; sputum reaction medium; anti-Escherichia coli O157 immunization Magnetic beads; modified peptone buffer, 0.01 mol/L, pH 7.2; physiological saline; Kovac's é› matrix reagent; Escherichia coli O157 antiserum.
Third, the experimental method
1, sampling
Take (x) g or (x) mL sample into 9(x) g or 9(x) mL mTSB + N enrichment solution and incubate at 41.5 °C. The final sample has a volume ratio of mTSB + N of 1: 10.
2, increase bacteria
The above-mentioned enrichment liquid was cultured at 41.5 ° C for 6 h, and then cultured for another 12 - 18 h for a total of 18 - 24 h. The subsequent immunological separation after 6 h culture and the false positive results obtained by inoculation on selective medium may give a negative result after 18 h culture.
3. Immunomagnetic separation (IMS)
Mix the enrichment solution and discard the residue of the food.
Take a centrifuge tube and add 20 μL of prepared immunomagnetic beads that are equilibrated to room temperature. Take 1 mL of the supernatant from the enrichment solution to avoid inhaling physical impurities or fat into the centrifuge tube. The suspension was mixed for 10 min at a rate of 12 - 20 r/min on a rotary mixer.
Place the tube on the magnetic rack and collect the beads to ensure that the beads are not absorbed on the tube wall. Open the tube cap (the tube is held on the magnetic rack) and use a sterile Pasteur pipette to slowly draw the liquid from the bottom of the tube. Each sample uses a new straw. Add 1 mL of sterile buffer solution to cover the tube cap, remove the tube from the magnetic rack, mix it upside down, and put it back into the magnetic rack.
Repeat the above cleaning process several times.
Finally, add 100 μL of sterile buffered cleaning solution to resuspend the beads and remove them from the magnetic rack.
4, vaccination
Aspirate 50 μL of the suspension onto the pre-dried CT-SMAC and use a sterile inoculation loop to obtain a well-separated single colony.
Incubate at 37 ° C for 18 - 24 h.
On the CT-SMAC plate, the typical colony morphology was transparent or nearly colorless, with yellow-brown around the colonies and a colony diameter of 1 mm.
5, diagnosed
5.1 Choosing colonies
Select 5 typical colonies on each plate, and select if all the typical colonies are less than 5. A typical colony was isolated and purified on nutrient agar. Incubate at 37 ° C for 18 - 24 h. Pure colonies should be used for identification.
5.2 Biochemical identification: å²å“š reaction
A purified single colony was picked from tryptone medium. Incubate at 37 ° C for 24 h. Add 1 mL of Kovac's é› matrix reagent and let stand for 10 min at room temperature. A red ring is positive, and a yellow ring is negative.
5.3 Serum diagnosis
Only colonies that are positive for sputum need to undergo Escherichia coli O157 serum reaction.
Drop a drop of normal saline on a clean glass slide, pick a colony on the nutrient agar on the nutrient agar, so that the colonies are evenly dispersed in the physiological saline, shake the slide for 30 - 60 s, observe on a black background. . If the bacterial suspension forms a mass, the strain is an autoagglutination strain and cannot be tested for a specific antiserum.
The pure colonies on the nutrient agar were picked up on a glass slide, suspended in physiological saline, and a drop of Escherichia coli O157 antiserum was added dropwise. If agglutination occurs within 1 min, the reaction is positive.
Colonies are positive for sputum and meet O157 antiserum or O157:H7 antisera positive. Colonies can be identified as Escherichia coli O157.
6, quality control
6.1 Quality Control Strains
The non-toxic Escherichia coli O157 strain can be obtained from the National Collection of Cultures, which can be used for quality control of culture media and serum.
6.2 Training methods
Prepare a low-level, pathogenic Escherichia coli O157 reference sample for testing laboratory capabilities and testing methods for testing low-level Escherichia coli O157 in accordance with the test methods described in this international standard. Parallel testing was performed with a sample that added a large amount of other Escherichia coli.
7. Detection limit and reporting limit
According to the results, Escherichia coli O157 was detected or not detected according to the method in the specified mass or volume sample.
In the detection of pathogenic bacteria and the total number of colonies including Escherichia coli O157, pure water is required for the steps of medium preparation, reagent preparation and the like. RephiLe especially recommends the Direct-Pure UP integrated ultrapure water system. Direct-Pure UP is an ultrapure water system that uses tap water as the influent water while producing RO pure water and ultrapure water. The ultra-pure water produced by Direct-Pure UP is sterilized by a dual-wavelength UV lamp and decomposed with organic matter. After being trapped by a 0.22 μm terminal filter, the bacterial content in ultrapure water is less than 1 cfu/mL, which can be used to prepare medium and reagent solution; RO pure Water can be used to clean laboratory vessels and water baths. Direct-Pure UP can be equipped with a water pick-up handle. RephiLe's unique patented water-receiving built-in resistivity detector can reflect the real water quality of the water intake point in real time. The handle connection is up to 3 meters long, and the remote water intake is easy and comfortable. RephiLe can also provide verification services for pure water systems to help users complete ISO, GMP, and GLP-compliant system verification to meet the laboratory's requirements for certification activities. Make sure you are at ease, safe, and worry-free.
About RephiLe:
RephiLe is a professional manufacturer and supplier of water purification and laboratory separation and purification products with a strong technical background in laboratory water and filtration. RephiLe has gradually established its own product brand based on its own research and development results, driven by innovation and service-oriented. It has independent intellectual property rights and obtained a number of patents. The management concept of international operation, perfect and reliable quality monitoring and guarantee system make RephiLe's products high quality and reliable. Once entered the market, it is recognized and favored by the majority of users. It is at the high-end leading technology and quality level among similar products in China. RephiLe has cooperated with many leading technology institutions at home and abroad, and its products are sold to more than 80 countries in Europe and America.
For more information on RephiLe products, please visit: RephiLe official website
Official Weibo: RephiLe Weibo
Official blog: RephiLe blog
RephiLe Enterprise WeChat Name: Pure Water Hotline 400 690 0090
We're Professional Supplier Extract Powder manufacturers and suppliers in China specialized in providing high-quality products at low price. We warmly welcome you to buy or wholesale bulk Supplier Extract Powder for sale here from our factory. For a free sample, contact us now.
Supplier Extract Powder,Supplier Extract ,Supplier Powder Manufacturer in China
Shaanxi Kang New Pharmaceutical co., Ltd. , https://www.apipepdite.com